
Typical reaction conditions are pH 4.0-4.5, 60 ☌, and a carbohydrate concentration of 30-35% by weight. In the second step, known as "saccharification", the partially hydrolyzed starch is completely hydrolyzed to glucose using the glucoamylase enzyme from the fungus Aspergillus niger. This heat treatment improves the solubility of starch in water, but deactivates the enzyme, and fresh enzyme must be added to the mixture after each heating. Some variations on this process briefly heat the starch mixture to 130 C or hotter one or more times. Over the course of 1-2 hours near 100 ☌, these enzymes hydrolyze starch into smaller carbohydrates containing on average 5-10 glucose units each. In the United States, cornstarch (from maize) is used almost exclusively. Maize, rice, wheat, potato, cassava, arrowroot, and sago are all used in various parts of the world. Many crops can be used as the source of starch.
Glucose is produced commercially via the enzymatic hydrolysis of starch.

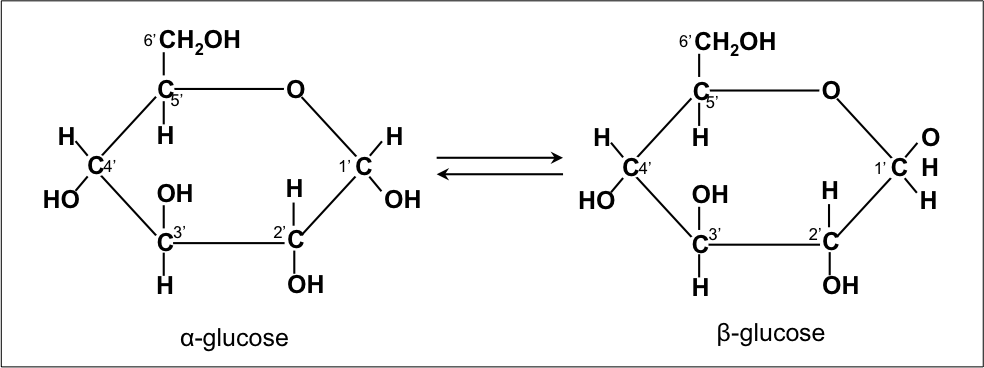
The α and β forms interconvert over a timescale of hours in aqueous solution, to a final stable ratio of α: β 36:64, in a process called mutarotation. When D-glucose is drawn as a Haworth projection, the designation αmeans that the hydroxyl group attached to C-1 is below the plane of the ring, β means it is above. They differ structurally in the orientation of the hydroxyl group linked to C-1 in the ring. These eight isomers (including glucose itself) are all diastereoisomers in relation to each other and all belong to the D-series.Īn additional asymmetric center at C-1 (called the anomeric carbon atom) is created when glucose cyclizes and two ring structures, called anomers, can be formed — α-glucose and β-glucose. Only 7 of these are found in living organisms, of which D-glucose (Glu), D-galactose (Gal) and D-mannose (Man) are the most important. Glucose is one of these sugars, and L and D-glucose are two of the stereoisomers. These are split into two groups, L and D, with 8 sugars in each. In this ring, each carbon is linked to an hydroxyl side group with the exception of the fifth atom, which links to a sixth carbon atom outside the ring, forming a CH2OH group.Īldohexose sugars have 4 chiral centers giving 24 = 16 optical stereoisomers. As the ring contains five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, which resembles the structure of pyran, the cyclic form of glucose is also referred to as glucopyranose. In water solution both forms are in equilibrium, and at pH 7 the cyclic one is the predominant. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) and ring (cyclic) form(in equilibrium), the latter being the result of an intramolecular reaction between the aldehyde C atom and the C-5 hydroxyl group to form an intramolecular hemiacetal. Glucose (C6H12O6) contains six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group and is therefore referred to as an aldohexose. The mirror-image of the molecule, L-glucose, cannot be used by cells. This article deals with the D-form of glucose. This form (D-glucose) is often referred to as dextrose ( dextrose monohydrate), especially in the food industry. Two isomers of the aldohexose sugars are known as glucose, only one of which (D-glucose) is biologically active. Glucose is one of the main products of photosynthesis and starts cellular respiration in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.

The cell uses it as a source of energy and metabolic intermediate. Glucose (Glc), a monosaccharide (or simple sugar), is the most important carbohydrate in biology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
